Direct Drive Motors
Ditch gearboxes and belts for peak efficiency in your AMRs. Direct drive gives pinpoint control, whisper-quiet runs, and zero-maintenance life for cutting-edge warehouses.

Core Concepts
High Torque Density
Pumps big torque straight to the load, no gear reduction—perfect for quick starts and heavy payloads in tight AGV designs.
Zero Backlash
No mechanical drivetrain means instant response, zero backlash, and sub-millimeter precision.
Silent Operation
Gear-free design slashes noise, ideal for hospital bots, offices, and anywhere quiet matters.
Maintenance Free
With fewer moving parts, you've got fewer chances for things to break. Kiss goodbye to lubing gears, swapping belts, or fiddling with tensioners—that means less downtime for your fleet.
Compact Integration
These motors are typically 'in-wheel' or slim 'pancake' designs, freeing up crucial space inside the chassis for batteries and computing gear.
Energy Efficiency
Ditching transmission friction boosts overall efficiency, stretching battery life and range on your mobile robots.
How It Works
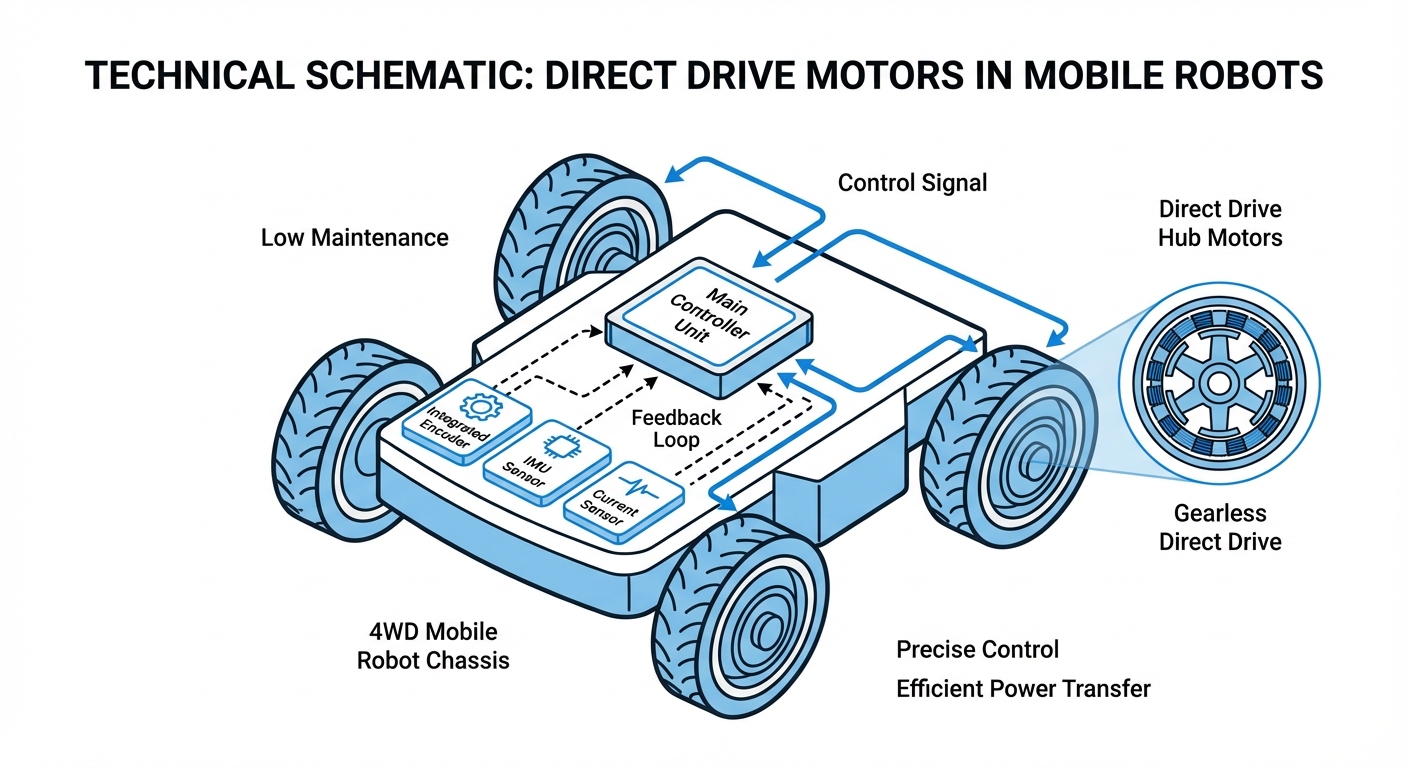
A Direct Drive Motor (often called a torque motor) works through direct magnetic interaction, with no mechanical go-betweens. The rotor slots right into the AGV's wheel hub, while the stator mounts to the chassis axle.
High-res optical or magnetic encoders attach straight to the shaft for real-time feedback to the servo controller. This handles fancy motion like instant stops or ultra-slow, buttery-smooth creeps needed for docking.
With the load coupled directly to the motor, the system's rigidity beats geared options hands down. It shrugs off bumps like a pro—the control loop snaps it back instantly, no gearbox 'slop' to blame.
Real-World Applications
Warehouse Logistics (AMRs)
Direct drive hubs are the gold standard for modern shelf-lifting robots. Their huge starting torque lets pint-sized bots hoist and haul 1000kg+ racks with silky acceleration.
Medical & Hospital Robots
In clean, hush-hush spots, gear racket is a no-go. Direct drive motors glide delivery carts and disinfection bots silently through patient wards.
Precision Inspection Platforms
Gear vibes can trash data on metrology and scanning robots. Direct drive delivers razor-smooth speed control to steady LiDAR and cameras.
Outdoor Delivery Rovers
Sealed direct drive units (IP65+) laugh off dust and water. No chains or exposed gears makes them perfect for sidewalk delivery bots battling Mother Nature.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between a Direct Drive and a Geared Motor?
The key difference? The transmission. Geared motors use a gearbox to dial down speed and crank up torque—but that adds friction, backlash, and upkeep hassles. Direct Drive motors link the load straight to the rotor, axing the gearbox for pure 1:1 motion transfer.
Are Direct Drive motors more expensive than traditional motors?
Sure, the motor itself might cost more upfront thanks to premium magnets and build quality. But Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) usually drops lower—no gearbox, belts, labor, or spare parts eating your budget over the robot's life.
How do Direct Drive motors handle heat dissipation?
They pump out big torque at low speeds, so cooling matters. Modern direct drive AGV motors feature huge surface areas or built-in heatsinks (fins) for passive heat dumping. Heavy-duty? Liquid cooling's available, but air cooling rules for mobile bots.
What is "cogging" and is it an issue with these motors?
Cogging's that choppy jerk at low speeds from rotor magnets tugging on stator teeth. Modern direct drive motors tame it with skewed stators and clever control algorithms, keeping motion glass-smooth even at < 1 RPM.
Can Direct Drive motors hold a load when powered off?
Nope, generally not. High-ratio gearboxes can self-lock, but direct drive spins free without power. For AGV safety on ramps, an electromechanical brake is standard in the motor to lock it down when power drops.
What type of motor controller do I need?
You need a beefy servo drive with sinusoidal commutation or Field Oriented Control (FOC). Trapezoidal block commutation usually falls short for direct drive's silky low-speed needs.
Is the weight of the motor a concern for mobile robots?
Direct drive motors can tip the scales more than a wee motor plus plastic gearbox, all that iron and copper for torque. But they swap out axles, transmissions, and bearings, so net weight barely budges—and it's low in the wheels for better stability.
What happens if the wheel hits an obstacle?
Direct drive shrugs off shock loads better than geared systems, where teeth can snap on impact. Still, spec your axle and bearings for the AGV's radial and axial forces.
Are these motors suitable for differential drive robots?
Absolutely. They're perfect for differential drive. Two independent wheels mean zero-radius turns and pinpoint odometry—must-haves for SLAM navigation.
What voltage ranges are typical for AGV direct drive motors?
Most AGV direct drive motors run low-voltage DC (24V, 48V, or 60V). Keeps everything in 'Safety Extra Low Voltage' (SELV) territory for easier safety certs and battery hookups.
Do I need a specific type of wheel tire?
Since the motor often doubles as the wheel hub, the tire (usually polyurethane or rubber) molds or bolts right onto the rotor. Choose a compound that grips the rim and floor without slipping under torque.
How long do these motors last?
Bearings are the only wear items in a direct drive motor. Sized and loaded right, they hit 20,000–30,000 hours easy, outlasting geared setups that need constant lube and gear swaps.