Warehouse Material Transport
Revolutionize your logistics with AMRs that smartly and safely move goods around the clock. Automate transport to slash costs, boost throughput, and perfect inventory tracking.
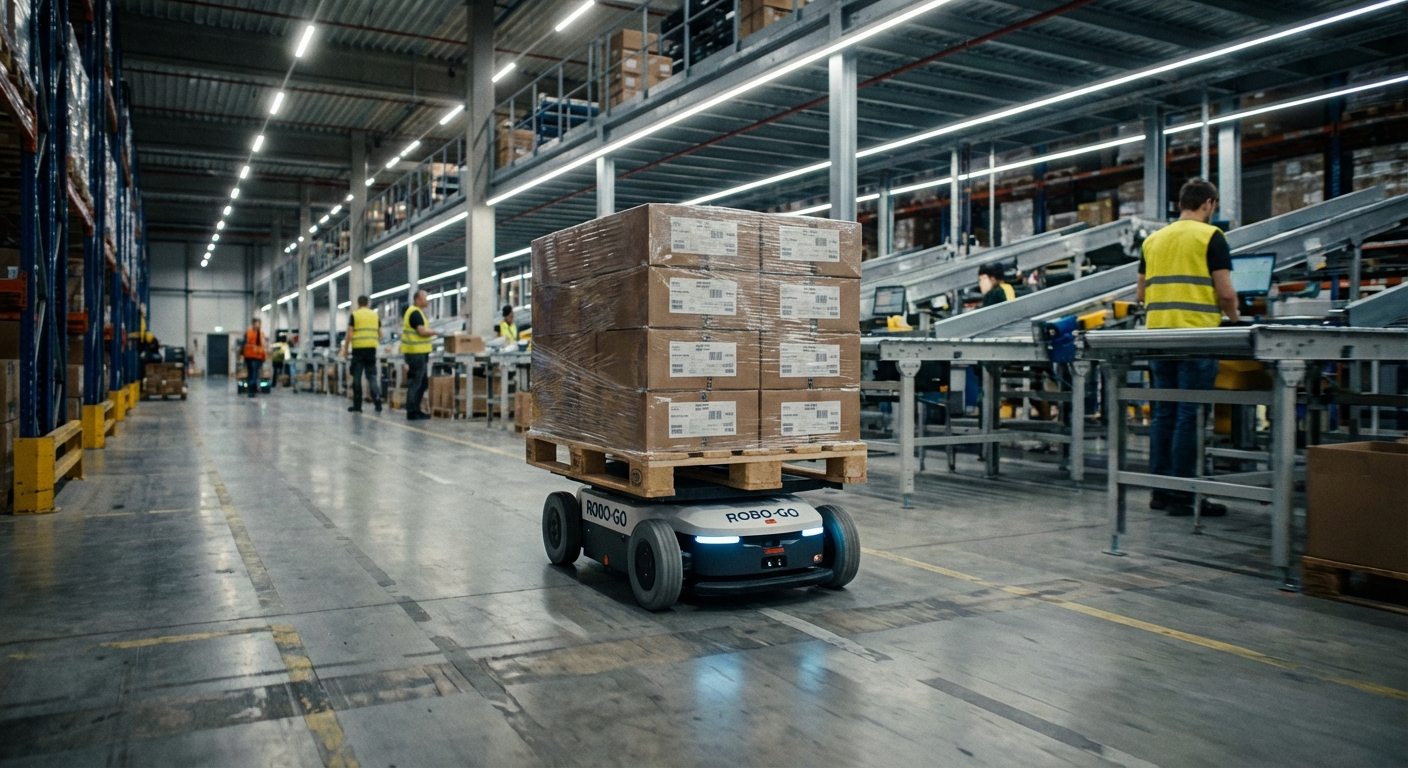

Why Automate Warehouse Material Transport?
Increased Efficiency
No fatigue means non-stop operation, with real-time route adjustments for faster deliveries and more per hour.
Enhanced Safety
LiDAR and vision tech let them dodge people and obstacles, slashing accidents far below manual forklifts.
Labor Optimization
Shift workers from grunt transport to smarter tasks like QC and picking, reducing turnover and burnout.
Accuracy & Traceability
Seamlessly ties into your WMS for full digital tracking—no lost inventory or shipping slip-ups.
Cost Reduction
Cuts costs by eliminating temp labor, minimizing facility damage, and lowering maintenance.
Flexible Scalability
Easily scale your fleet for peaks without retraining or major changes.
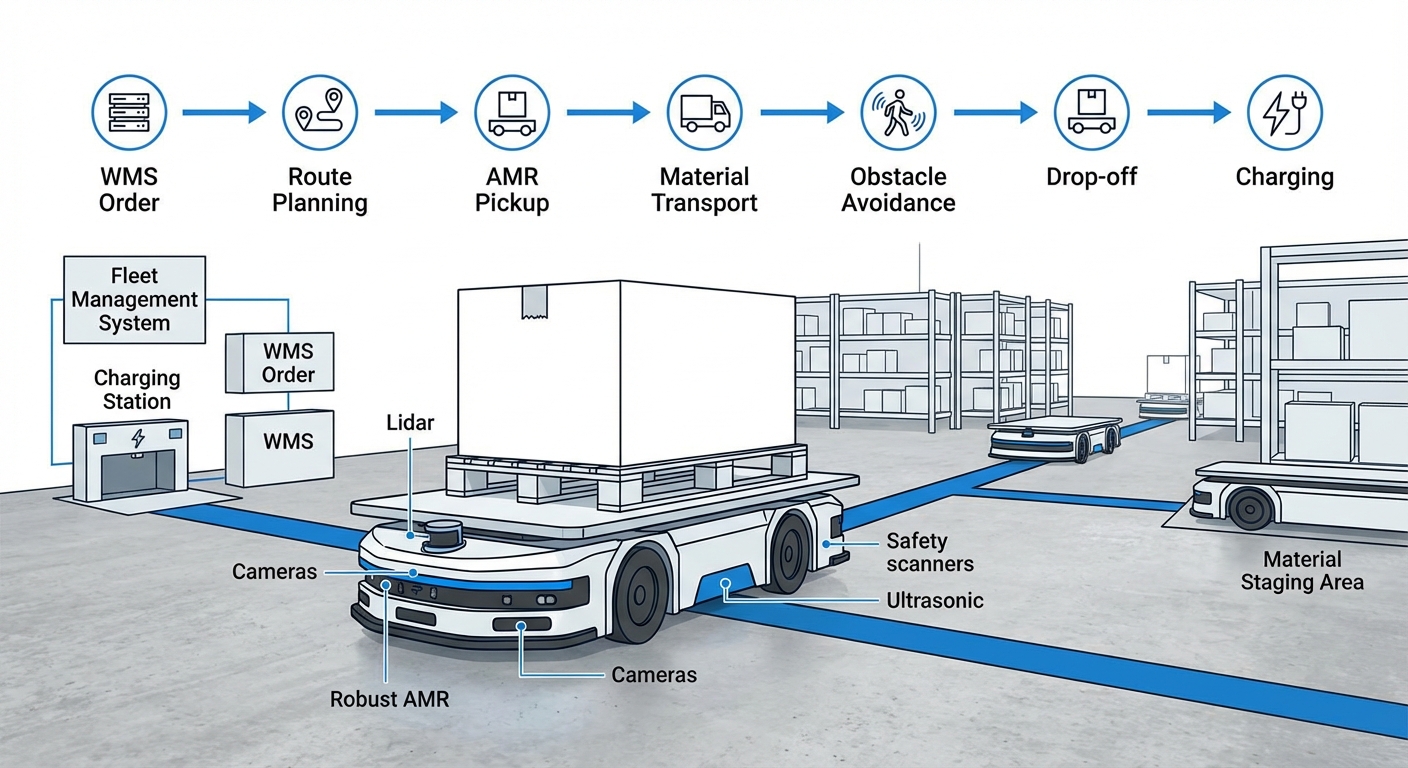
Intelligent Navigation & Coordination
SLAM tech is the core—robots digitally map your space for free-roaming navigation, no tape required.
Fleet Management System orchestrates it all, pulling WMS orders, assigning bots, avoiding jams, timing charges, and managing elevators.
At the destination, they connect to conveyors or arms for seamless autonomous pick-up and drop-off.
Where It's Used
E-commerce Fulfillment
Goods-to-person: brings shelves right to pickers, cutting walk time by 70%.
Automotive Manufacturing
Just-in-time parts delivery to production lines, keeping stations stocked but lean.
3PL Logistics
Shuttle pallets from docks to storage to shipping for efficient cross-docking.
Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
Safe, clean transport of meds, samples, linens in hospitals.
What You Need
Hardware & Infrastructure
- Flat, clean flooring (concrete or industrial coating)
- High-speed Wi-Fi (WiFi 6 preferred) or Private 5G network
- Charging stations (Auto-docking power supply)
- Designated staging areas for pickup/drop-off
Software Stack
- Fleet Management System (FMS) server
- API Integration with WMS/ERP (REST/VDA 5050)
- Map editing and route planning interface
- Analytics dashboard for performance tracking